

Electromagnetic Fields (EMF)
Sources Of Radiation
Our world is becoming digital, devices or equipment at home such as Microwave ovens, computers, televisions, Wi-Fi routers, cellphones, Bluetooth & etc. are common sources of EMFs. Even we suffer EMF radiation emitted from our neighbors, Power station and cell towers near us.
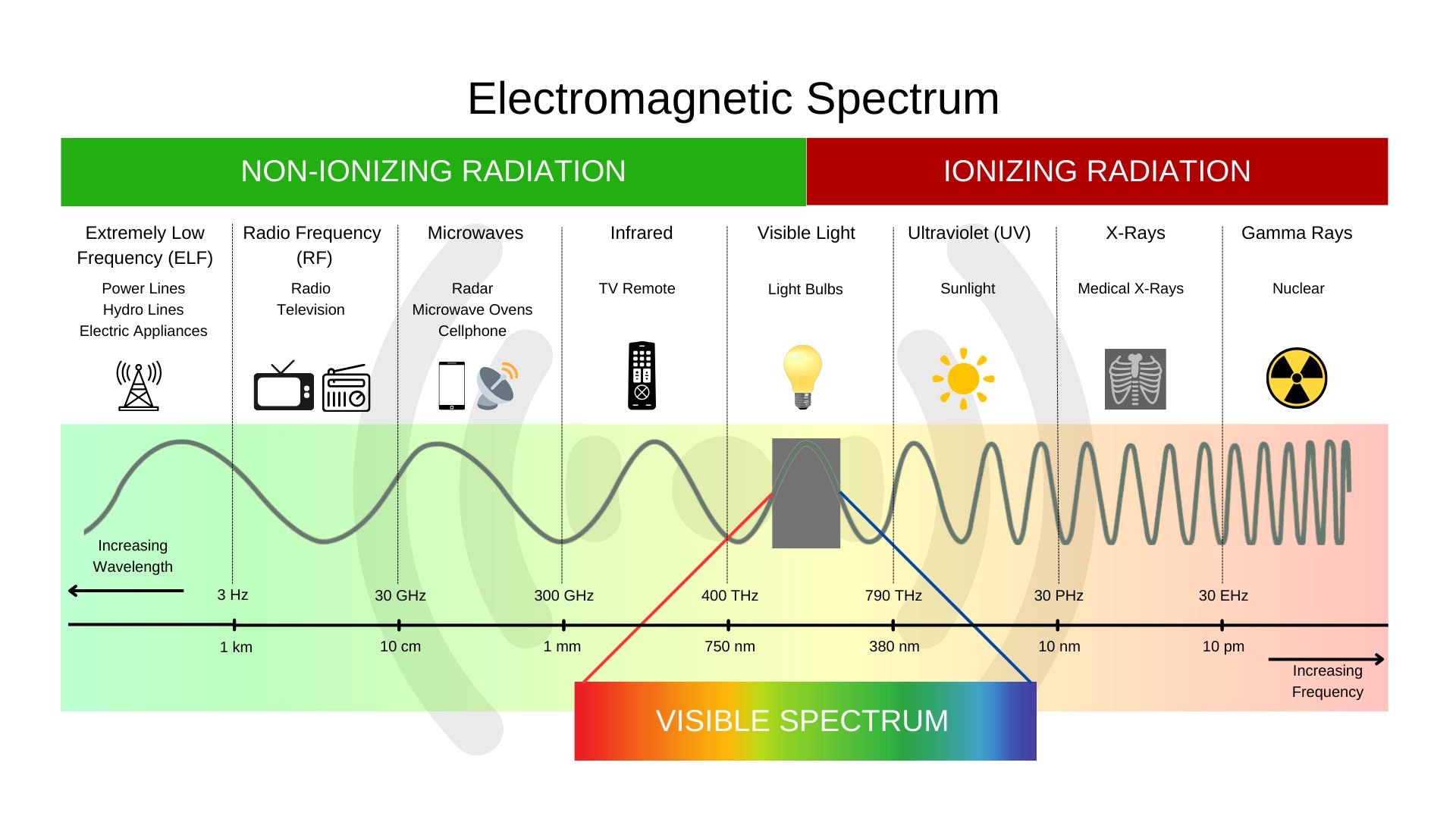
Non-ionizing EMF:
These are electromagnetic fields with frequencies lower than those of visible light. Non-ionizing EMFs are typically produced by common household appliances, power lines, and wireless devices such as cell phones and Wi-Fi routers. They are generally considered to be of lower energy and are not powerful enough to break chemical bonds in molecules, hence the term “non-ionizing.”
Ionizing EMF:
These electromagnetic fields have higher frequencies and energies than non-ionizing EMFs. Examples include X-rays, gamma rays, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ionizing EMFs have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, leading to the formation of ions. Exposure to ionizing radiation can pose health risks, including an increased risk of cancer, if not properly managed and controlled.
Understanding these categories helps in assessing the potential risks associated with different types of electromagnetic fields and in implementing appropriate safety measures when necessary.
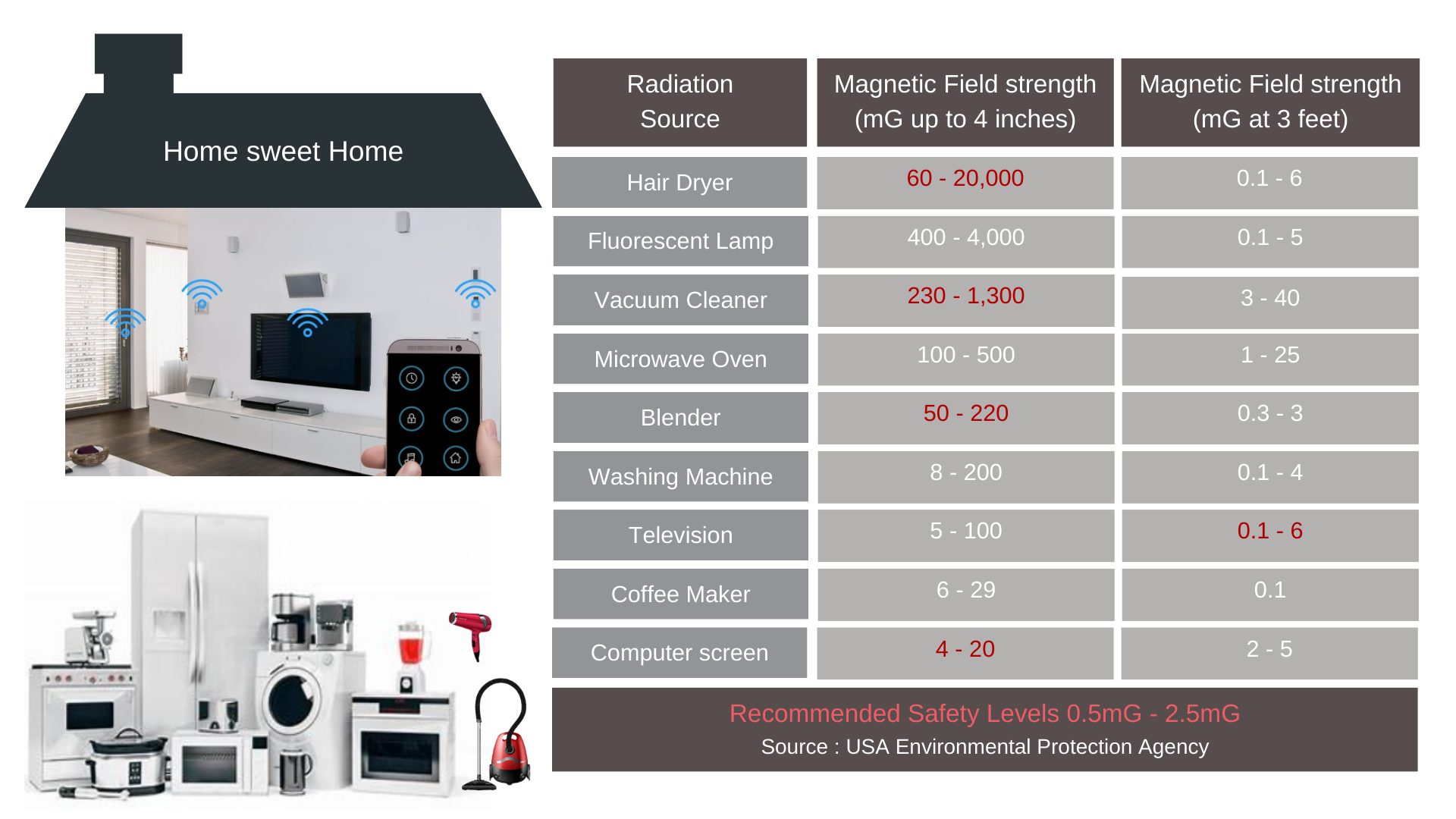
Health Risks of Electromagnetic Radiation

How to Mitigate Exposure to EMFs?


